ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Systems Interactions and Changes 3 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Systems Interactions and Changes. What emf is introduced in the coil?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you here's your shmoop du jour brought to you
- 00:05
by smashing guitars it's an old rock'n'roll tradition but we
- 00:09
can't afford to buy a new guitar all the time
- 00:10
so we just smash our air guitars like that Well
- 00:14
carrie is playing air guitar in her room imagining that
Full Transcript
- 00:16
she's playing in front of a huge crowd She powers
- 00:19
through a sweet riff and the crowd goes wild Carrie
- 00:22
starts showboating swinging or guitar around around it flies off
- 00:26
the strap and smashes into the wall Talked about a
- 00:28
reality check She sorts through the pieces and notices that
- 00:32
the guitar pick up is a square coil of wire
- 00:36
Well maybe the broken guitar could be a science project
- 00:39
after all Science fair's coming up right Carrie flips open
- 00:42
her tax book looks for the words coil and finds
- 00:45
a page describing faraday's law According to this e m
- 00:48
f is induced in a coil within turns by a
- 00:52
change in magnetic floods In time carrie counts two hundred
- 00:57
turns in the coil and measures this side's as one
- 01:01
centimeter she places the coil in a uniform magnetic field
- 01:04
that points into the plane of the page Take a
- 01:08
look at this diagram right there Carrie increases be from
- 01:12
point Oh won t two point oh sixty in delta
- 01:15
t equals one s what imf is induced in the
- 01:19
coil and hear the potential answers one ten hundred thousand
- 01:24
when life hands you lemons while you make lemonade and
- 01:27
when life hands you a smashed guitar you make a
- 01:29
science project yeah we're pretty punk rock not so punk
- 01:33
rock that we have our own magnetic field generator though
- 01:36
kerry has quite the setup here right let's look at
- 01:39
magnetic flux First of all magnetic flux means the amount
- 01:43
of magnetic field passing through an area waken Think of
- 01:46
it like the density of a magnetic field in this
- 01:48
certain space so we can swap out b a for
- 01:52
the flocks which means our equation now shows the imf
- 01:55
equals the number of coils times the change in b
- 01:58
a over the change in time And since the area
- 02:01
is not changing we can bring that out Hang with
- 02:05
him Carrie increases the byfield from point Oh won t
- 02:09
two point oh sixty So the change in b equals
- 02:13
point Oh five tesla's Now we can plug in our
- 02:17
numbers and get back to rock in the house Mm
- 02:20
equals two hundred coils times one centimeter squared times point
- 02:24
oh five tesla's over one second Don't forget that with
- 02:28
an area of one centimeter squared it comes toh one
- 02:31
times ten to the negative forthe meters squared after we
- 02:34
do the math we find that the magnitude of imf
- 02:36
created is one mil eval So the correct answer is
- 02:39
a oh and one last thing way used a version
- 02:42
of faraday's law that cheats just a little bit faraday's
- 02:45
law expressed in this equation really should have a negative
- 02:48
sign in front of it negative sinus part of lens
- 02:51
law and it works to show the direction the current
- 02:54
needs to move in order to create a magnetic field
- 02:57
that opposes the change in floods But because this question
- 03:01
is really just dealing with the magnitude of voltage we
- 03:05
don't need to worry about the direction so don't tell
- 03:07
anyone but yeah we just broke the law one thrill
- 03:10
and remember to be careful with musical instruments They're meant
- 03:12
to make beautiful music that we don't want to be
- 03:15
smash guitars or broken drums that's or even a dented 00:03:18.22 --> [endTime] kazoo that matter
Up Next
Related Videos
AP Physics 2: 1.1 Properties of Objects and Systems. What is the magnitude and direction of the conventional current in this wire?
AP Physics 2: 1.5 Properties of Objects and Systems. According to the Bohr's model of the atom, which of the following are true?
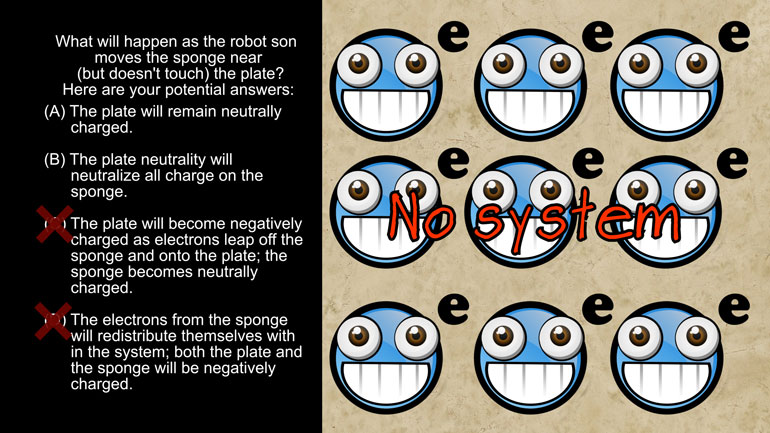
AP Physics 2: 2.2 Properties of Objects and Systems. What will happen as the robot son moves the sponge near (but doesn't touch) the plate?
AP Physics 2: 2.4 Properties of Objects and Systems. How could you show the carnival barker an emission spectrum?