ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Physics 1: 3.3 Object Interaction and Forces 174 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Physics 1: 3.3 Object Interaction and Forces. What is the minimum acceleration needed for the box to remain attached to the van?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak and here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by vans which just aren't as groovy
- 00:08
as they used to be Check the falling image and
- 00:12
passage Nice hair glasses in your stuff All right What
- 00:20
is the minimum acceleration that aunt gertrude would have to
Full Transcript
- 00:23
maintain in order for the box to remain attached to
- 00:26
the van and hear the potential answers all about friction
- 00:30
Uh no There's A lot going on in this question
- 00:33
Well let's try to make it simpler on ourselves by
- 00:35
drawn up the little force diagram right here Okay we've
- 00:40
got one force the van going in the ex direction
- 00:43
And this question will label that in for normal force
- 00:47
to calculate that force we use our trusty formula force
- 00:50
equals mass times acceleration Then we have to force is
- 00:53
in the y direction there's gravity pulling down on the
- 00:56
box and friction pushing it up In order for the
- 00:59
box to not fall these two forces have to balance
- 01:02
each other out So the force along the y axis
- 01:05
is equal to mass times gravity plus friction Well because
- 01:09
the forces air acting in different directions the first part
- 01:12
of the equation mass times gravity will be expressed as
- 01:16
a negative number and here's the equation All right Well
- 01:19
now let's deal with the friction in our scenario here
- 01:22
The normal force in is pushing back Against the box
- 01:25
the normal force and the coefficient of friction together create
- 01:28
the friction force Here The equation is friction is less
- 01:32
than or equal to the coefficient of friction times the
- 01:36
normal force in the equation musa bass represents the coefficient
- 01:41
of static friction it's important to remember that the question
- 01:45
is asking us to find the minimum acceleration needed to
- 01:48
hold the box in place If the normal force is
- 01:51
too small the friction force won't be strong enough to
- 01:53
balance out gravity in the box and fall But if
- 01:56
gertrud floors it jacking the normal force way up a
- 02:00
friction force will reduce that's because the normal course would
- 02:03
be pushing on the box so hard that the friction
- 02:05
force wouldn't have to be doing this much That's why
- 02:08
the equation has a lesser than or equal to sign
- 02:11
since we need to find the minimum force needed for
- 02:14
gertrude to make this crazy scheme work that means that
- 02:17
friction force needs to be at its highest possible point
- 02:20
Thor equation for four should really have an equal sign
- 02:24
okay quick reminder We're trying to balance the forces in
- 02:27
the uae direction the equation to use is force equals
- 02:31
the product of negative mass and gravity plus the product
- 02:35
of the coefficient of friction and the normal force And
- 02:38
normal force equals mass times acceleration Lastly the result of
- 02:43
our equation is zero because the forces balance each other
- 02:46
out right When we simplify the equation and solve for
- 02:50
acceleration we see that acceleration equals gravity divided by the
- 02:54
coefficient of friction for ten meters per second squared divided
- 02:58
by zero point six which comes out to about sixteen
- 03:02
point seven meters per second squared making option D The
- 03:06
correct answer And we're thinking of trading in our van 00:03:09.02 --> [endTime] for something easier to parallel park
Up Next
AP Physics 1: 2.5 Changes and Conservation Law. At what point(s) in this situation is energy lost in any form?
Related Videos
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
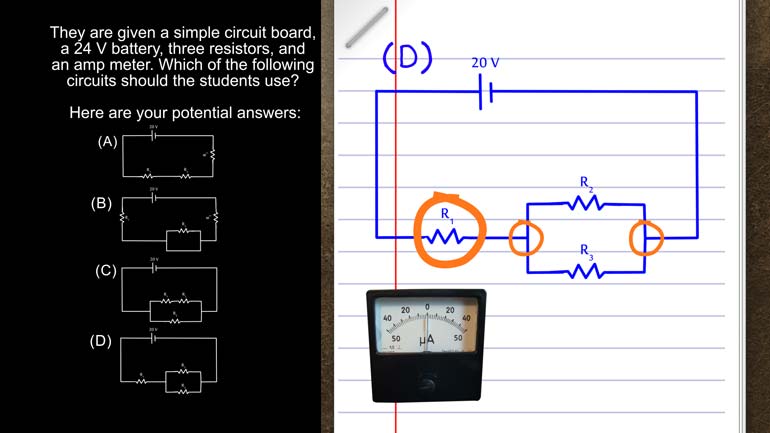
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?