ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Evolution Videos 10 videos
AP Biology 2.3 Evolution. What did the Urey-Miller experiments do?
AP Biology 4.1 Evolution. When or where is allopatric speciation likely seen?
AP Biology 2.4 Evolution 7 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Biology 2.4 Evolution. Since the human appendix can be removed without any any ill consequences, many scientists believe it is what?
Transcript
- 00:04
Here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by ill consequences.
- 00:07
We bet they’d feel better with a big bowl of chicken noodle soup. [Consequeces in bed with a bowl of chicken noodle soup]
- 00:11
Check out the following statement…
- 00:14
Because the human appendix can often be removed without any ill consequences, many scientists
- 00:18
believe it is this.
Full Transcript
- 00:21
And here are the potential answers: Let’s start with A, homologous structures.
- 00:28
Take a look at your hand. [Man looks at own hand]
- 00:29
You can grab, point, wave, hit, and hold, all with the help of your handy-dandy hand.
- 00:34
That’s how human hands evolved, and it’s a good thing they did…they come in handy [Man gesturing with hand while in traffic]
- 00:38
during rush hour traffic.
- 00:39
…Not that we do that, or anything.
- 00:42
But take a look at this seal. [A seal riding a car]
- 00:45
Not only is this seal a far better driver…his “hands” evolved into flippers, which help
- 00:51
him swim.
- 00:54
So even though our hands have similar bones, muscles and nerves when compared to seal’s
- 00:59
flippers, they perform different functions.
- 01:01
A seal’s flippers and human hands are examples of homologous structures. [A man and seal dancing]
- 01:05
They have similar anatomy, but different functions.
- 01:08
And considering the appendix can be removed without any ill consequences, we know that
- 01:12
it has no function, so we can eliminate A. So what about “B”?
- 01:15
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in different geographic
- 01:21
spaces.
- 01:22
The last time we checked, the appendix wasn’t occupying any geographic spaces, so we can [Man checking a map for appendix]
- 01:27
safely eliminate B. What about “D,” comparative embryology?
- 01:31
Comparative embryology compares and contrasts the fetal stages of different species.
- 01:37
The Greek philosopher Aristotle is considered to be the world’s first comparative embryologist. [Aristotle appears in a library]
- 01:42
In his writings, Aristotle mentioned “eggs” and “live births,” but surprisingly enough,
- 01:48
never spoke of the appendix…
- 01:50
Not even…in the appendix... [A list of words in an appendix]
- 01:51
Sorry.
- 01:52
Anyway, we can eliminate “D.” Looks like “C” is our answer.
- 01:55
Throughout human evolution, certain organs in the body have lost their original functions.
- 02:00
Look at the tailbone. [A man showing a tail bone]
- 02:01
When our tails fell off, the tailbone became vestigial, or functionless.
- 02:03
It’s a shame, though.
- 02:05
If we still had a tail, we’d always have something to do when we’re bored. [Man chasing a tail]
- 02:08
The appendix suffers the same sad fate as the tailbone.
- 02:11
Good bacteria is stored in the appendix and used to help fight off the effects of dysentery
- 02:15
and cholera.
- 02:16
However, since those ailments are harder to catch these days than the 6:25 a.m. school [School bus arrives]
- 02:21
bus, the appendix has long since lost its function, making it a vestigial organ.
- 02:25
But don’t worry, vestigial organs.
- 02:28
If Simon and Garfunkle can have two comebacks and the Eagles can have five... so can you. [Vestigial organs playing in a band]
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
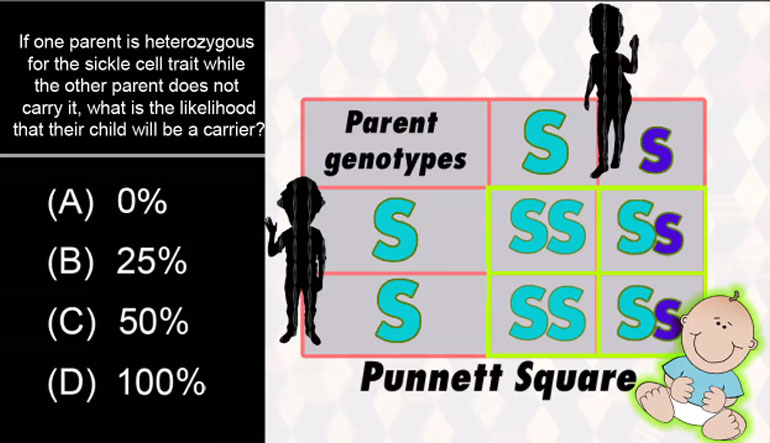
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?