ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
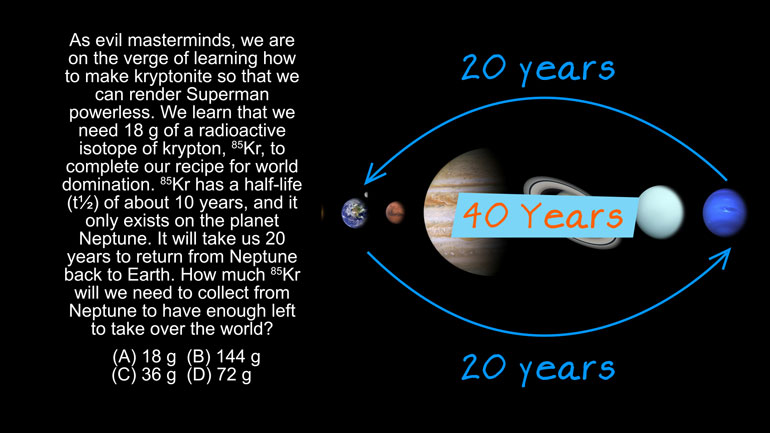
AP Chemistry Videos 54 videos
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
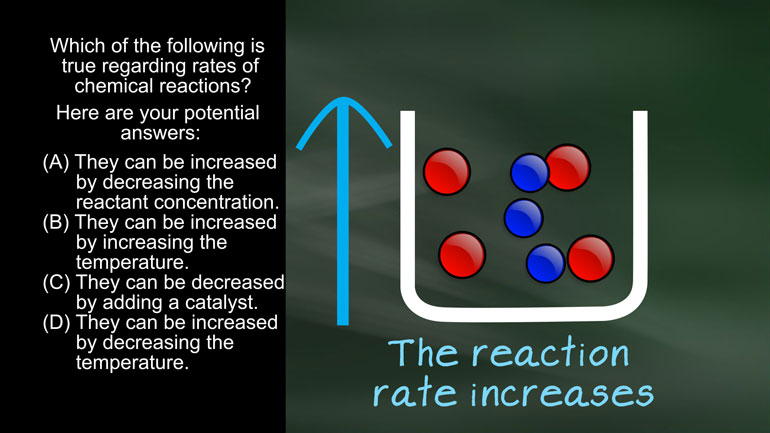
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?
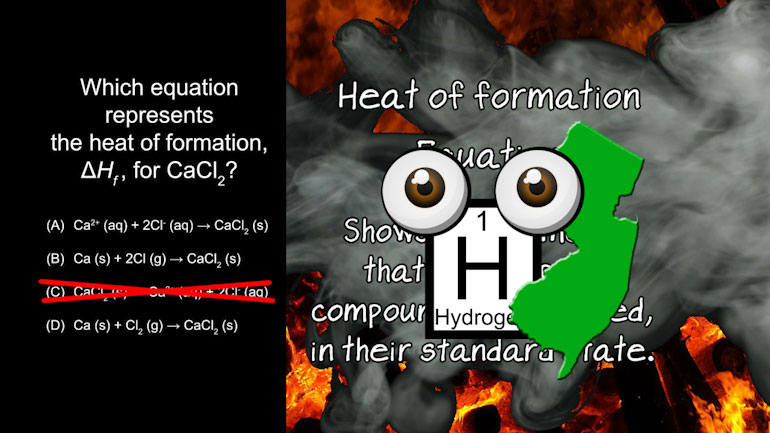
AP Chemistry 2.4 Laws of Thermodynamics 11 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Chemistry 2.4 Laws of Thermodynamics. What are the signs of ΔG, ΔH, and ΔS?
Transcript
- 00:04
And here's your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by the smoke machine, your weird uncle [Man smoking outside]
- 00:08
with a pack-a-day habit.
- 00:10
Okay, here's our question.
- 00:12
Solid CO2 is known as dry ice and is used in smoke machines and to keep food cold.
- 00:17
For the process at 25 °C: CO2 (s) ? CO2 (g)
Full Transcript
- 00:24
What are the signs of ?G, ?H, and ?S
- 00:28
And here are our potential answers.
- 00:30
All right, what’s this question asking us? [Girl thinking about the question]
- 00:34
Well, it requires us to think about the thermodynamics of the solid to gas phase change for CO2.
- 00:40
Let’s think about what the sign of ?G, ?H, and ?S mean
- 00:46
qualitatively.
- 00:47
First up - ?G, or the change in Gibbs free energy. [Gibb's free energy table]
- 00:50
No relation to Barry, Robin, or Maurice.
- 00:52
We know that ?G tells us about the spontaneity of a chemical reaction.
- 00:57
Like whether or not the chemical reaction will take a spur of the moment trip to Disneyland [Man on a rollercoaster in DisneyLand]
- 01:01
with you.
- 01:02
We hope so…we've been waiting to wear our mouse ears for years now…
- 01:04
Anyway, if the ?G is negative, the reaction is spontaneous.
- 01:08
Now what about ?H, or the change in enthalpy?
- 01:11
The sign of ?H tells us if a reaction is endothermic or exothermic. [DeltaG sign with exothermic or endothermic]
- 01:16
A positive change in enthalpy implies that the reaction is endothermic and absorbs heat,
- 01:23
while a negative change in enthalpy implies that the reaction is exothermic and releases
- 01:28
heat.
- 01:29
As far as blankets go, you want the endothermic ones. [A dog wrapped in a blanket]
- 01:32
Anyone selling you an exothermic blanket is a bad guy..
- 01:36
And finally ?S, or the change in entropy.
- 01:40
Entropy tells us about the degree of dispersal, or disorder.
- 01:43
A positive change in entropy means that entropy has increased, and thus disorder has increased.
- 01:50
Your messy room? [Boy in a messy bedroom]
- 01:51
That’s a very positive change in entropy.
- 01:54
Now that we have this handy dandy chart, the problem becomes a lot easier.
- 01:58
That’s right, take it all in. [Man studying the chart]
- 02:00
We're pretty sure this chart is in contention to be the eighth wonder of the world…
- 02:03
… it's okay to cry.
- 02:04
Okay, so let’s consider our specific “reaction,” which is just a phase change: [Scientist drops substance into a beaker]
- 02:08
CO2 (s) ? CO2 (g)
- 02:13
We want to decide if each variable in our chart is positive or negative for this reaction. [Girl sat waiting]
- 02:17
Let’s walk through it.
- 02:18
And yes, we'll do it hand in hand.
- 02:20
Safety first.
- 02:21
Is our reaction spontaneous?
- 02:23
Yes—it happens at 25°C without any effort from us. [Pregnancy stick with 25 degrees shown]
- 02:27
Easy, breezy, beautiful.
- 02:29
Chemical reactions.
- 02:30
Is our reaction endothermic or exothermic?
- 02:33
AKA does it absorb or release heat? [fire burning]
- 02:35
Well, if it’s used to keep food cold, it must absorb heat from the food.
- 02:41
Thus, the reaction is endothermic.
- 02:44
And finally, is our reaction product, a gas, more or less disordered than our reactant,
- 02:49
a solid?
- 02:51
Gas molecules are further apart and more dispersed. [Gas bellowing]
- 02:53
Thus, they are more disordered than molecules in a solid.
- 02:57
We don’t blame them.
- 02:58
Everybody gets a little crazy when they’re far away from their pals. [Gas on a doctor's bed and doctor appears]
- 03:01
Now, looking at our handy chart, we see that ?G is negative, ?H is
- 03:05
positive, and ?S is positive.
- 03:08
So let’s mosey on down back to our potential answers…
- 03:11
It looks like choice (C) is the one we’re looking for. [Answer C circled and C dances in a club]
- 03:13
It’s okay, choice C, we can’t all be positive all of the time.
- 03:16
2 out of 3 times ain't half bad.
Related Videos
AP Chemistry 3.2 Laws of Thermodynamics. What is the value for ΔG?
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?