ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Standard Data Structures Videos 18 videos
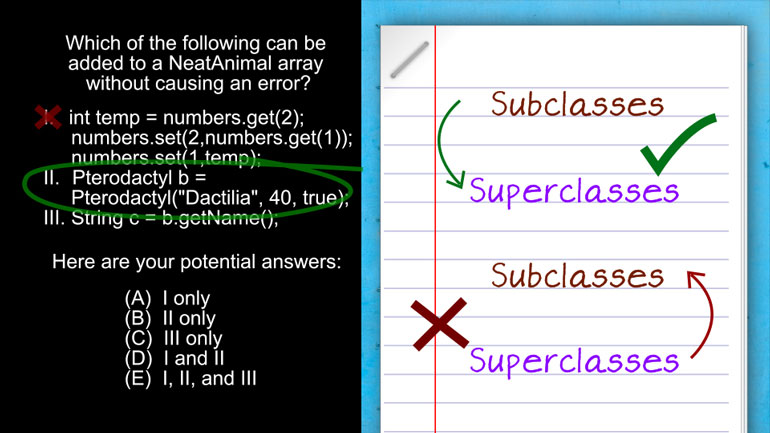
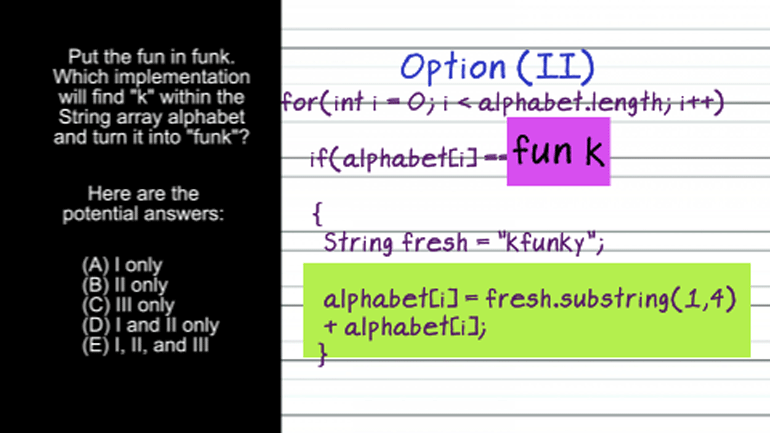
APCS: Standard Data Structures Drill 1, Problem 2. Which of the following methods are not appropriate for reuse in other programs?
AP Computer Science 3.2 Standard Data Structures. Which of the following methods successfully add an element to the array?
AP Computer Science: Standard Data Structures Drill 3, Problem 5. The resulting array from this code snippet has which of the following shapes?
AP Computer Science 4.1 Standard Data Structure 8 Views
Share It!
Description:
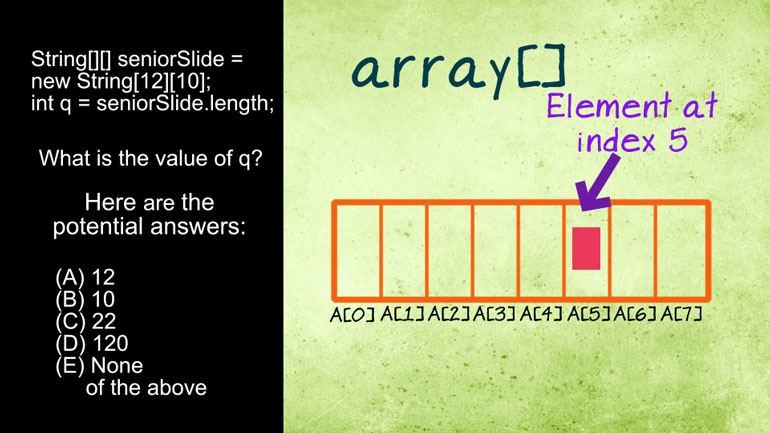
AP Computer Science 4.1 Standard Data Structure. Can you find the value of q?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak And here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:06
Brought to you by multi dimensional arrays They're not just
- 00:09
a scifi alien weapon anymore What is the value of
- 00:13
q and hear your potential answers All even Numbers 1
- 00:18
through here Well quick Visualize an array of eight elements
Full Transcript
- 00:22
Do it Got it Yeah Pretty simple It's A little
- 00:25
like a number line about with data sitting on it
- 00:27
That and to refer to any element you can call
- 00:30
it by its index What if you want another road
- 00:33
data Well sure you could make a whole new separate
- 00:35
array but that's little clunky This is more of a
- 00:38
Job 4A:2 dimensional array at an extra set of brackets
- 00:41
and well off we go We can reference anything in
- 00:44
this array by using it to indices horizontal and vertical
- 00:47
or clever names x and why i want to get
- 00:51
wild Well we can keep going on tow three dimensional
- 00:53
rays that are totally doable and learn our square into
- 00:56
a cube And again we'd be using the erase three
- 00:59
indices that weaken reference elements anywhere along its three axes
- 01:03
So now we have a three dimensional array full of
- 01:05
data Sounds very futuristic Already But we can go through
- 01:08
that What would a fourth dimension be like Where would
- 01:11
you put it Easy Well right next to it despite
- 01:14
the complaints from your businesses friends all right If a
- 01:17
one dimensional array gave us the number line two d
- 01:20
gave us a square and three d gives a cube
- 01:23
then forty is a number line made of cute haven't
- 01:27
we just blow your mind all right And a five
- 01:30
deer a while you guessed it A grid made of
- 01:33
q's sixty a cube made of cubes seventy a number
- 01:37
line made of a cube made of cubes You can
- 01:40
see where this is headed into infinity Well java language
- 01:43
specifications states you could theoretically have infinite dimensions but the
- 01:47
job of virtual machine the thing that actually executes code
- 01:51
sets a limit of two hundred fifty five dimensions thankfully
- 01:55
for our brains to need for that many dimensions doesn't
- 01:57
come up all that often In fact an array of
- 01:59
more than three dimensions is downright rare and this question
- 02:02
is asking us what the length of a certain two
- 02:04
dimensional array would be logically speaking since we're dealing with
- 02:08
a two d array It it makes sense to multiply
- 02:10
with times height like measuring erecting like twelve times ten
- 02:14
But that's not how the length function works in java
- 02:17
It returns simple inger based on the length of a
- 02:19
single dimension in this case the first dimension because we
- 02:22
didn't specify a deeper one That said the answer is 00:02:25.895 --> [endTime] right in front of our faces the entire time
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?