ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Waves Videos 15 videos
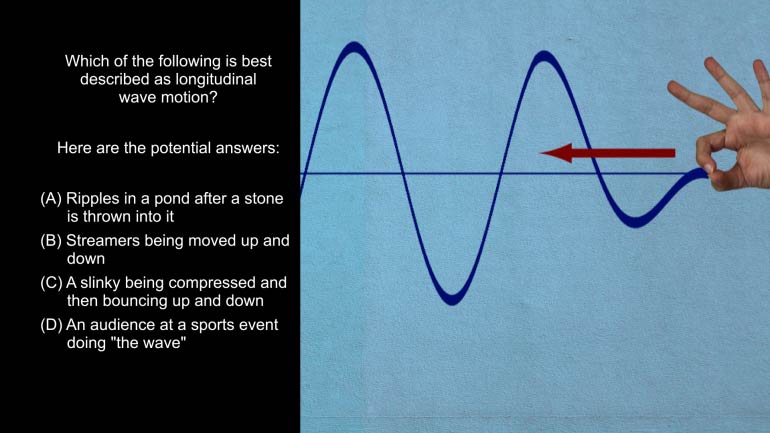
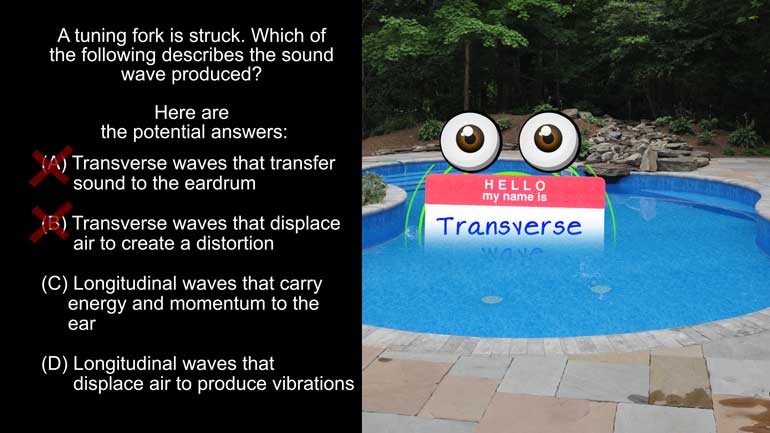
AP Physics 1: 2.3 Waves. Which of the following is best described as longitudinal wave motion?
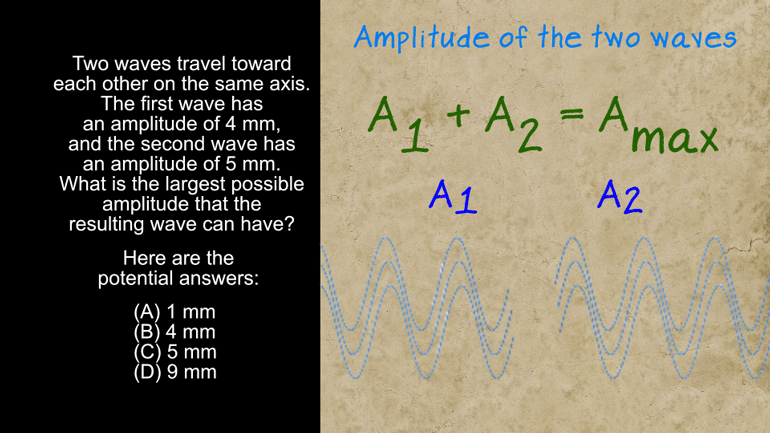
AP Physics 1: 2.1 Waves. What is the largest possible amplitude that the resulting wave can have?
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Waves 13 Views
Share It!
Description:
If you've ever listened to someone with coffee breath, you know that the closer they scoot, the more intense it gets. It's pretty much the same principle with radiation.
Transcript
- 00:01
No and here's your shmoop du jour brought to you
- 00:04
by intensity intensity can be a good thing especially when
- 00:09
we're getting ready for a big test But too much
- 00:11
intensity when we're studying can be a bad thing Even
- 00:14
we hear it smoking a little sleep well a longitudinal
Full Transcript
- 00:19
wave source lambda is located five meters to the left
- 00:23
of point x A trans verse wave source bro is
- 00:27
ten meters to the right of point x Both sources
- 00:30
emit s o tropic radiation of the same power What
- 00:35
can be said about the ratio of intensities measured at
- 00:39
point x All right here The potential answers Yes we
- 00:43
got all that intensity introduction thing Okay well we've got
- 00:46
trans verse waves We've got longitudinal waves We've got s
- 00:51
o tropic radiation This is like the start of a
- 00:54
superhero origin story or something But before we get to
- 00:58
the part where shmoop er man comes to earth let's
- 01:01
figure out how these intensities relate well ice A tropical
- 01:04
radiation emanates from a point source and it shoots out
- 01:08
in all directions with equal intensity Because of this fact
- 01:12
the farther we are from the source of radiation the
- 01:15
less the intensity we feel in fact intensity is proportional
- 01:20
to the inverse square of the distance from the source
- 01:24
of radiation So if one object a is twice a
- 01:28
ce far from a radiation source as object be than
- 01:32
object a will get hit with one quarter of the
- 01:36
radiation object b receives which means for our question since
- 01:40
object lambda is one half the distance from the source
- 01:43
of the radiation as object row the radiation received from
- 01:47
lambda will be four times higher So our answer is
- 01:51
a but let's run through the math Just to be
- 01:53
sure the leftward intensity is proportional to the inverse square
- 01:57
of the leftward radius and the right word intensity is
- 02:01
equal to the inverse square of the right word radius
- 02:04
since we're looking for the radius will set the leftward
- 02:07
intensity over the right word intensity With this complex fraction
- 02:11
it simplifies to the right word Distance squared over the
- 02:15
left word distance squared We just plug in our numbers
- 02:18
and sure enough we get same answer Leftward intensity is
- 02:21
four times higher and let's try to keep our studying
- 02:24
intensity at a reasonable level A five maybe a six
- 02:27
We've been at ten before and it wasn't pretty after
- 02:30
we woke up in the closet muttering about wave frequencies
- 02:34
Who decided Tto dial it back a bit and go 00:02:37.51 --> [endTime] decaf
Related Videos
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Waves. Which of the following is technically true for Max as he stands at the edge of oblivion?
AP Physics 1: 1.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Find the current across R2.
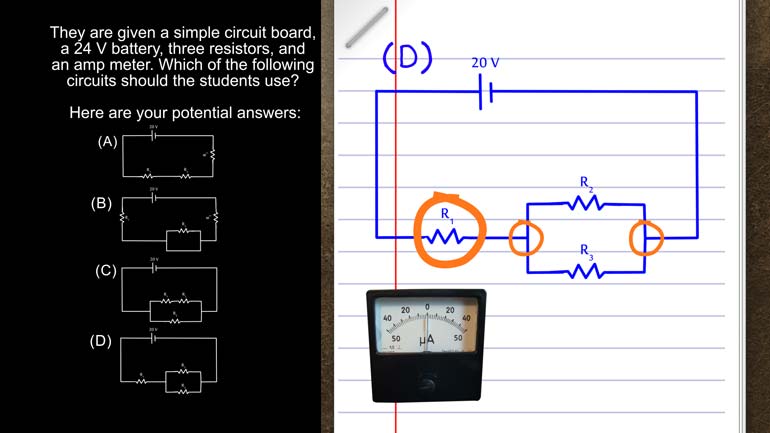
AP Physics 1: 2.4 Changes and Conservation Laws. Which of the following circuits should the students use?
AP Physics 1: 1.5 Waves. What can possibly occur when the two waves reach each other?
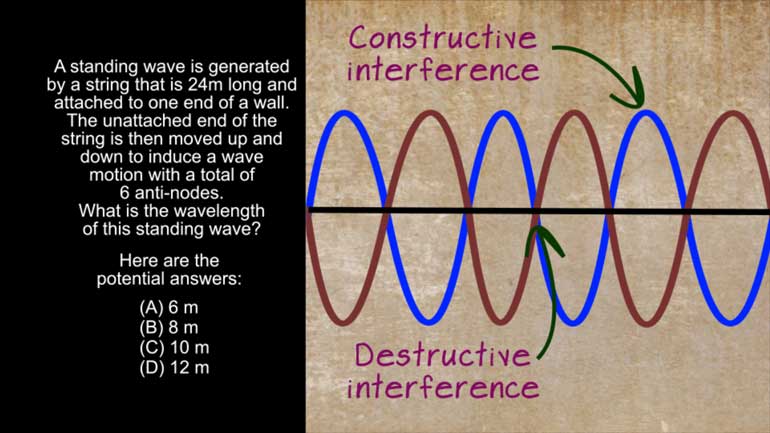
AP Physics 1: 2.2 Waves. What's the wavelength of this standing wave?