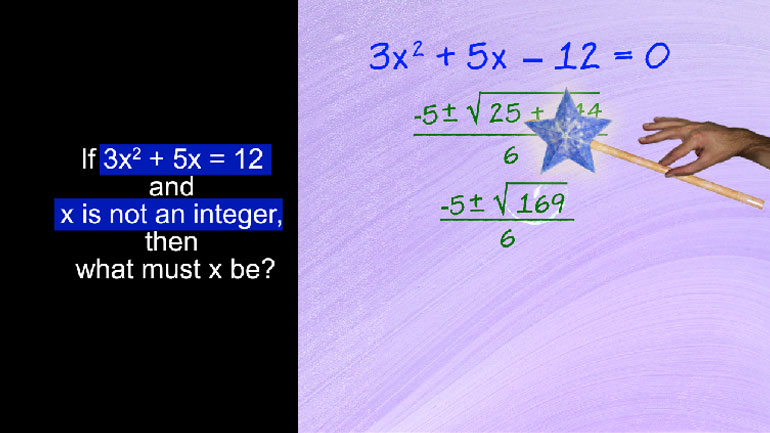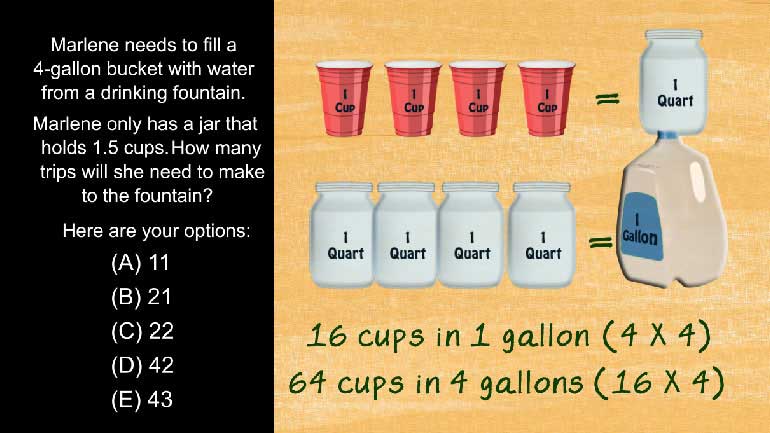ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Passport to Advanced Math Videos 52 videos
In the equation above, if a, b, and c are all constants, what is c?
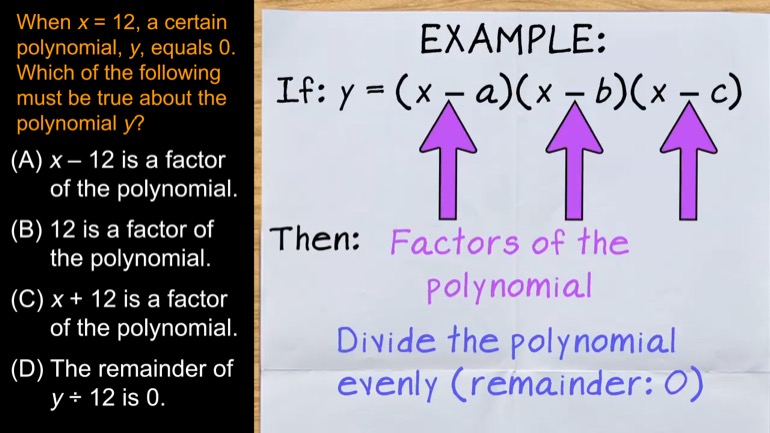
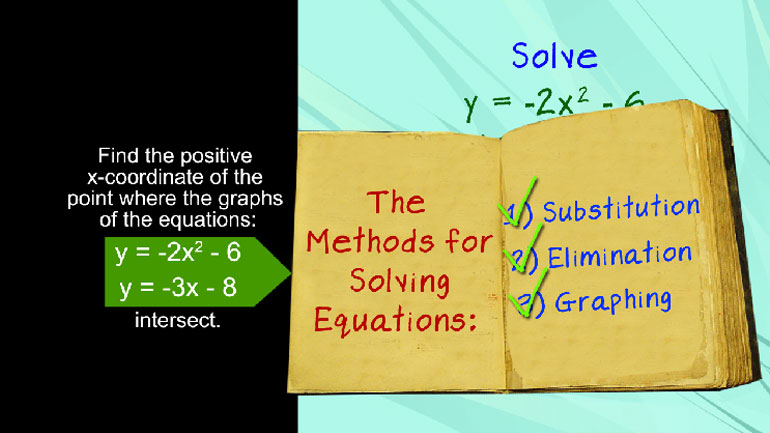
When x = 12, a certain polynomial, y, equals 0. Which of the following must be true about the polynomial y?
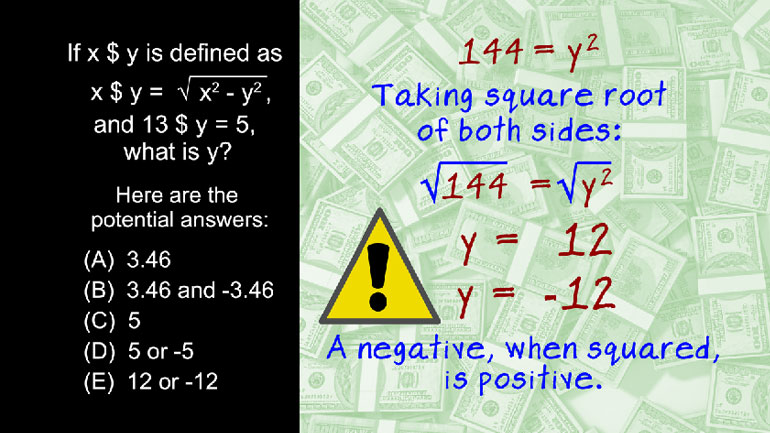
SAT Math 1.5 Algebra and Functions. If f (x) = x2 - 16 and g(x) = x4 - 256, what is f of x divided by g of x?
SAT Math 6.2 Algebra and Functions 268 Views
Share It!
Description:
SAT Math 6.2 Algebra and Functions
- Numbers and Operations / Squares and Square Roots
- Product Type / SAT Math
- Number and Quantity / Perform arithmetic operations with complex numbers
- Number and Quantity / Use complex numbers in polynomial identities and equations
- Number and Quantity / Perform arithmetic operations with complex numbers
- Number and Quantity / Use complex numbers in polynomial identities and equations
- Passport to Advanced Math / Radicals and rational exponents
Transcript
- 00:02
Here’s your shmoop du jour, brought to you by the square root symbol.
- 00:06
Not to be confused with the square root beer symbol.
- 00:12
If a = -64 and b = 64, which of the following are not real numbers?
- 00:19
And here are the potential answers…
- 00:23
Okay, so we know that a is -64, and b is 64.
Full Transcript
- 00:28
First off, we can substitute the values for a and b.
- 00:31
The first choice becomes the square root of -64.
- 00:34
The second becomes the square root of 64, the third becomes the cube root of -64, and
- 00:40
the fourth becomes the cube root of 64. Now, which of these are not real numbers?
- 00:45
Remember that a real number is something that exists on a number line.
- 00:48
That includes natural numbers, integers, and rational numbers.
- 00:53
What it doesn’t include is imaginary numbers. We get imaginary numbers when we try to take
- 00:58
an even root of a negative number.
- 01:04
If we look at option 1, it looks like we’re trying to take the square root of negative 64.
- 01:10
Well it's imaginary number, since no number squared can equal negative 64.
- 01:16
Which means option 1 is not a real number.
- 01:18
Roman numeral 2 is the square root of 64. Well… that’s easy. It’s just 8.
- 01:23
8 falls within the category of integer, which is a real number.
- 01:28
Option 3 is the cube root of -64.
- 01:31
Even though we’re taking the root of a negative number, this number does exists.
- 01:35
In fact, the cube root of -64 is just negative 4.
- 01:39
Finally, the cube root of 64.
- 01:41
The cube root of 64 is, in fact, 4. Choices 2, 3 and 4 all exist.
- 01:46
However, option number 1 is not a real number.
- 01:48
Our answer is (A).
Related Videos
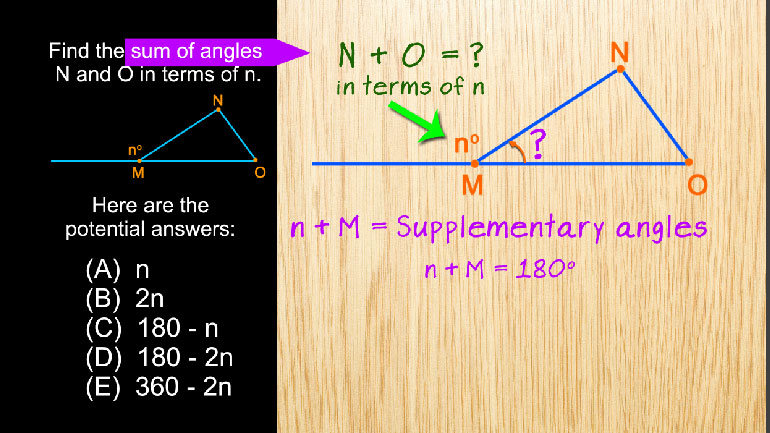
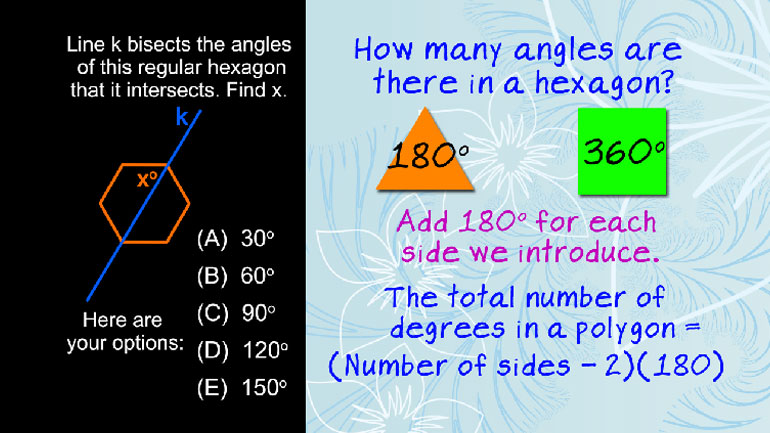
SAT Math 2.1 Geometry and Measurement. What is the measure of angle z in terms of x and y?
In 2014, the unemployment rate of one county in California was 7%. In another county, the unemployment rate was 11%. Which of the following express...
Angela is making cookies for a bake sale. She expects each batch of her cookies to sell for $40. It costs her $10 to make one batch of cookies, and...