ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Videos 1345 videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
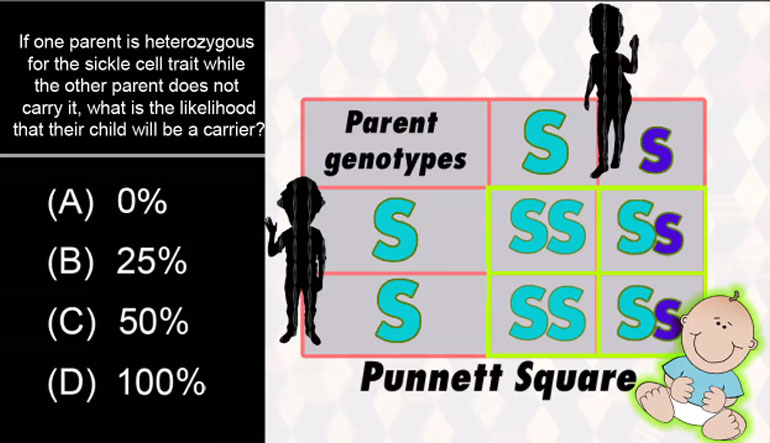
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology 3.3 Evolution 3 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Biology 3.3 Evolution. What is a small population of organisms prone to?
Transcript
- 00:04
Here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by small populations.
- 00:07
If that describes your Twitter following, you may want to consider tweeting about more [James Smith's twitter following page]
- 00:12
exciting topics.
- 00:13
And no, corn is not exciting.
- 00:15
All right, let's take a look at the question…
Full Transcript
- 00:17
A small population of organisms is prone to...what?
- 00:21
And here are the potential answers
- 00:28
Let's start at the very beginning. [Caveman starting a fire]
- 00:30
We hear it's a very good place to start.
- 00:32
Mutation is a natural process that changes a DNA sequence and the precise order of nucleotides
- 00:38
within a DNA molecule.
- 00:40
It's also the reason why it's safe to say that no two people are alike. [Two guys take off their hats]
- 00:43
So all this time you've called your little brother a mutant?
- 00:46
You're not too far off base. [Family sitting down for dinner]
- 00:48
Random genetic changes have little or no effect on a small population of organisms making
- 00:53
“A” incorrect.
- 00:55
Moving on to “B,” nonrandom mating. [A couple kissing]
- 00:58
Nonrandom mating occurs within organisms when there are plenty of potential mates to choose
- 01:02
from.
- 01:03
It's provides the opportunity within a large gene pool to pick out a mate based on compatibility, [A large swimming pool]
- 01:09
or desirable traits.
- 01:10
In a small population, there’s no chance to pick and choose.
- 01:14
All you can do is hope your mate likes death metal, because it’s all random selection. [Man picking a mate]
- 01:19
All of this means that “B” is the wrong answer.
- 01:21
How about D, high migration rates?
- 01:23
Well, there's nothing that indicates that a small population has any more desire to
- 01:27
pick up and move than a larger population would. [Baby deer prancing in a field]
- 01:30
That's not to say it wouldn't happen given the right circumstance.
- 01:33
Sometimes you end up with high rent, or irritating neighbors.
- 01:37
So while a small population may be prone to migration, it is not prone to high migration
- 01:43
rates, which means answer “D” is incorrect.
- 01:46
Which leaves us with “C”.
- 01:48
Genetic drift is the change in the frequency of a gene variant. [Graph depicting change in frequency of a gene variant]
- 01:52
The smaller the population, the more susceptible it is to dramatic changes in gene frequencies.
- 01:58
In other words, genetic drift can determine whether an individual within a small population
- 02:03
reproduces or even survives.
- 02:06
Genetic drift can have a large impact on a very small population, meaning that C is the
- 02:09
correct answer.
- 02:11
And seriously.
- 02:12
Stop tweeting about corn. [Man tweeting about corn on his mobile]
- 02:14
No one should care this much about corn. Seriously, come on people.
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?