ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Videos 1345 videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
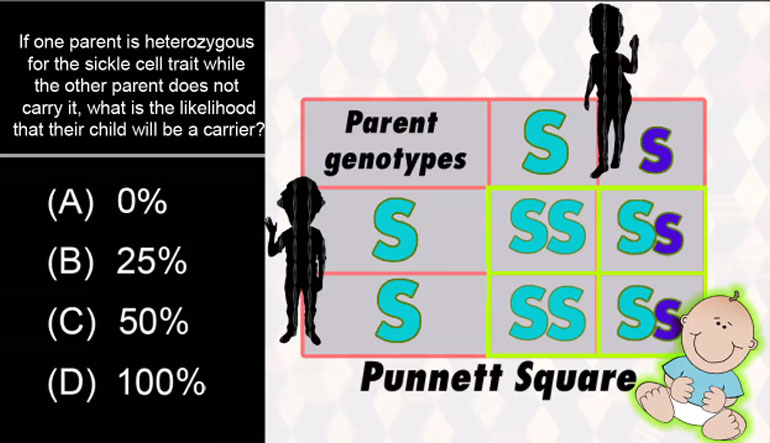
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Chemistry 3.5 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms 55 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Chemistry 3.5 Structure and Arrangement of Atoms. Which of the following is true regarding solids?
Transcript
- 00:03
Here’s your Shmoop du jour, brought to you by medicinal chemistry.
- 00:07
If you can’t helium, and you can’t curium, you’ll just have to barium [Two guys on a table entertaining people in a restaurant]
- 00:11
Here’s our question…
- 00:16
Which of the following is true regarding solids?
- 00:18
And here are our potential answers…
Full Transcript
- 00:25
Let's start at the top with (A).
- 00:27
(A) just means that all the stuff in a solid is in a very small space.
- 00:31
Does that seem true?
- 00:32
Well, if you’ve ever vaporized anything in the microwave, let’s say a grape, you [A microwave and a bunch of grapes appear]
- 00:36
probably know that if you put a solid object in and heat it to make a gas or a plasma,
- 00:41
it will often expand to fill the microwave. [Microwave explodes and grapes hit a man in the face]
- 00:44
Not that…we've tried this before….ahem.
- 00:48
Anyway, it seems like A might be a reasonable choice, so we'll come back to it. [Car drives down a road]
- 00:52
The next answer says that solids have the highest average kinetic energy relative to
- 00:56
liquids and gases.
- 00:58
Average kinetic energy is what temperature measures. [Thermometer gauge rising]
- 01:00
A high temperature means a high average kinetic energy, and a low temperature means a low
- 01:05
average kinetic energy.
- 01:06
This means the question is actually asking us if solids are generally hotter than liquids [A log of wood, rain and gas]
- 01:11
and gases.
- 01:12
Although having gas is not hot when you’re on a date, gases themselves are the hottest [Man farts walking through a park with a girl]
- 01:16
state of matter on average.
- 01:18
Temperature-wise.
- 01:19
We don’t know how they fare in online dating… [Mobile phone with a Tinder picture of a gas]
- 01:22
Solids are colder than both liquids and gases in fact, so we can cross off choice B right away.
- 01:28
Let’s move on to answer C, which says that the particles are in a randomly assorted 3D
- 01:33
structure, brought to you by Oculus [An oculus rift AI headset]
- 01:35
As much as your Lego kit at home may be in disarray, the atoms within each Lego piece [Boy surrounded by lego pieces]
- 01:40
should be arranged fairly regularly compared to a liquid or a gas….unless you’ve run
- 01:45
your Legos through a particle accelerator. [Pieces of lego shooting through a particle accelerator]
- 01:47
Maybe you have, maybe you haven’t.
- 01:49
…Don't try that at home either.
- 01:51
So answer C is off the table.
- 01:53
Moving on to answer D. [Car drives past a sign labelled 'D']
- 01:55
This next statement says that solids have a definite volume from an indefinite shape.
- 02:00
If you take a sugar cube as an example, you can see that a solid has a very definite volume
- 02:04
as well as a definite shape. [A sugar cube in a kitchen]
- 02:05
if you pound the cube into dust, it still has a definite shape. [Hammer smashes sugar cube to dust]
- 02:10
It’s just gone from a cube to an amorphous pile of dust that has no geometric name.
- 02:16
So answer D is off the table because indefinite shape does not describe solids.
- 02:20
That leaves us with our original answer A, that solids constitute a condensed state of
- 02:24
matter.
- 02:25
So it looks like nothing was the matter with answer A… [Guys cheering in a pub]
- 02:29
…We'll see ourselves out.
Related Videos
AP Chemistry 1.3 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the overall order of the reaction?
AP Chemistry 1.4 Chemical Reaction Rates. What are the correct units for a second order rate constant?
AP Chemistry 1.5 Chemical Reaction Rates. What is the rate law for the reaction?
AP Chemistry 3.2 Laws of Thermodynamics. What is the value for ΔG?