ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Psychology Videos 135 videos
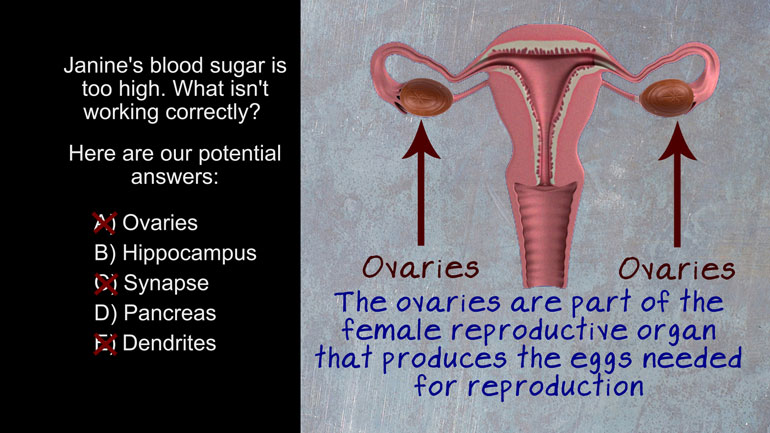
AP Psychology 1.1 Sensation and Perception. The process by which the brain can turn sensory stimuli from the outside world into electrical signals...
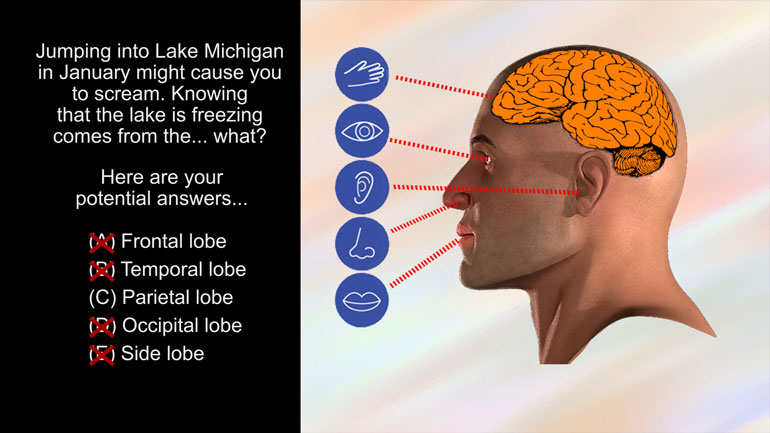
AP Psychology 1.1 States of Consciousness. Who conducted research on REM sleep deprivations?
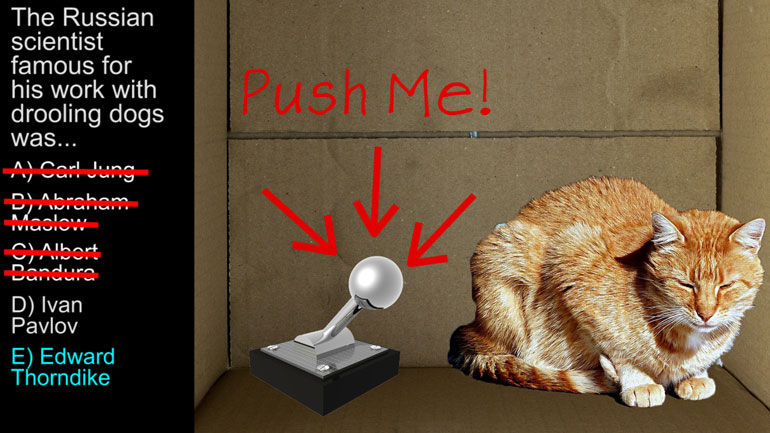
What is Pavlovian conditioning, and should you apply it before rubbing in your Pavlovian shampoo? Watch this vid to find out.
AP Psychology 3.3 Cognition 3 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Psychology 3.3 Cognition. What is the difference in the way the problem is presented referred to as?
Transcript
- 00:04
And here's your shmoop du jour brought to you by $1,000,000 these
- 00:08
shmoop teachers are getting pricey so into will wait for a Black Friday deal [Little girl putting coins in piggy bank]
- 00:12
all right here's a question Joe and Mike are asked to think of creative ways that
- 00:16
save the company 1 million dollars next year
- 00:18
Joe is told that a solution is needed quickly or many people will lose their
Full Transcript
- 00:22
jobs while Mike is told that a quick solution is needed so that the jobs of
- 00:26
many people can be saved the difference in the way that the problem is presented
- 00:31
is referred to as what ?
- 00:36
all right 1 million a lot of pressure we'd really hate to be Joe and Mike [Joe and Mike appear together]
- 00:40
right now so what's the difference between Joe and Mike trying to save
- 00:43
people jobs and Joe and Mike trying to stop people from losing their jobs
- 00:46
answer nothing but the distinction that Joe and Mike's bosses are making is a [Joe and Mike's boss appears in office]
- 00:52
conscious one but how would we describe it well not with the term fixedness
- 00:56
that's for sure functional fixedness is a cognitive bias
- 01:00
that limits them individual to using an object in the way it's normally used so
- 01:05
let's say Joe and Mike were tasked with popping a bunch of balloons and they [Balloons appear in a box]
- 01:08
came across a fork while Joe and Mike experienced functional fixedness they [Joe and Mike popping balloons]
- 01:13
would say that the fork couldn't possibly be used for popping balloons
- 01:16
because it's only used for eating food let's go in Mike these balloons well [Man eating a balloon]
- 01:21
this is in our answer but hey we're not judging what you want guys you're the
- 01:25
million dollar idea man the answer isn't see either a mental set describes the
- 01:30
way in which we group problems in order to see solutions for similar problems
- 01:34
from the past well if Joe and Mike were instead tasked
- 01:37
with opening a stuck jelly jar they might recall that running a jar under [Man attempts to open jelly jar]
- 01:41
hot water worked last time and they'd assume this would work again mental says [Jar thrown into hot water]
- 01:45
however sometimes lead people away from seeing more obvious solutions like the
- 01:49
arrows indicating to twist the other way and this that's the brightest bulbs
- 01:53
today go and microwave well D) anchoring
- 01:57
describes the cognitive bias where and people rely too heavily on the first
- 02:00
piece of information they receive and then anchor into it so if we first said
- 02:04
to Joe and Mike that we clean out their gutters for $200 they think it was a [Lots of leaves stuffed into a gutter]
- 02:09
ridiculous prize sure but they be anchored into thinking it's a price we
- 02:13
realistically want so we'd scale down a bit because we're
- 02:16
nice people and Joe and Mike would think they were given an awesome deal but [Joe and Mike look at anchor in shop window]
- 02:20
ultimately cleaning up gutters is something people do for less than an
- 02:23
eighth of our first price anchoring a great tactic for used-car salesmen and
- 02:28
sailors alike but not our answer and adjustment describes the way we balance
- 02:32
conflicting needs if we're peelin Thursday we adjust our behavior to take [Joe takes sip of water]
- 02:36
the water and meet that need if we're tired we find a way to get some rest and [Mike sleeping]
- 02:40
for hungry left we're even enjoy a package of Oreos that's the immediate
- 02:44
success so E is not what we're looking for well that just leaves us with a
- 02:48
framing framing describes the way in which a problem is presented or framed
- 02:53
depending on the framing of a problem humans can be motivated or limited in [Man inspecting problem in a frame]
- 02:56
their creativity in general humans don't like taking risk
- 03:00
so when problems are presented in terms of a loss like it was the joke
- 03:04
he's far less likely to take risk or be creative but because Mike's problem was
- 03:08
framed in terms of saving jobs he's more inclined to get creative with a solution [Mike appears and dogs parachute either side of him]
- 03:12
because there's no risk of loss looming over his head some generalists best of
- 03:16
frame problems in the most neutral way possible so a is the correct answer
- 03:20
let's definitely guys are still snacking on jelly covered balloons and what [Joe and Mike eating balloons]
- 03:24
company might want to look elsewhere for a million-dollar solution just a thought
Related Videos
AP Psychology 1.1 Social Psychology. Which of the following best describes social psychology?
AP Psychology 1.1 States of Consciousness. Who conducted research on REM sleep deprivations?
AP Psychology 1.2 Cognition. Which of the following strategies would work best for generating new ideas?
AP Psychology 1.2 Sensation and Perception. The cells in the back of the eye that only see in black and white are called what?
AP Psychology 1.2 Social Psychology. What is the best choice for producing better productivity?