ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
AP Psychology Videos 135 videos
AP Psychology 1.1 Sensation and Perception. The process by which the brain can turn sensory stimuli from the outside world into electrical signals...
AP Psychology 1.1 States of Consciousness. Who conducted research on REM sleep deprivations?
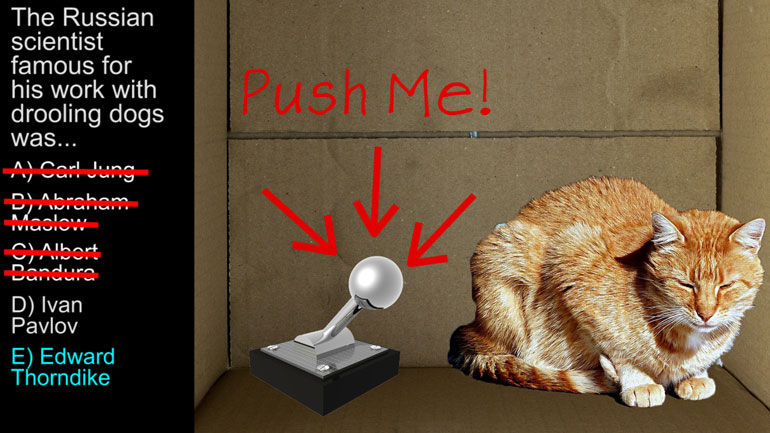
What is Pavlovian conditioning, and should you apply it before rubbing in your Pavlovian shampoo? Watch this vid to find out.
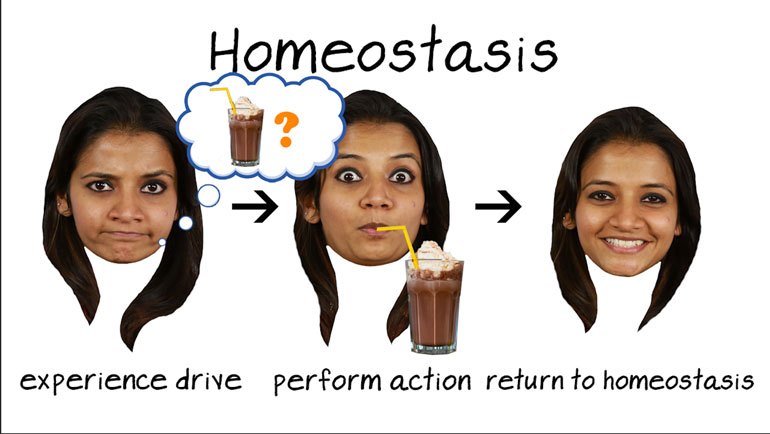
AP Psychology 3.3 Motivation and Emotion 17 Views
Share It!
Description:
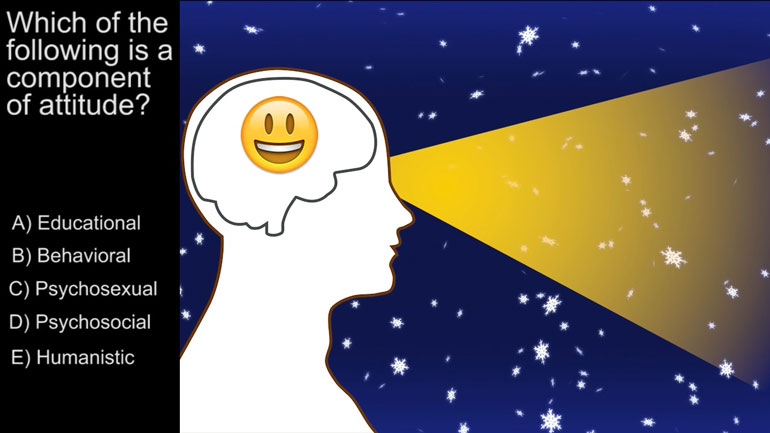
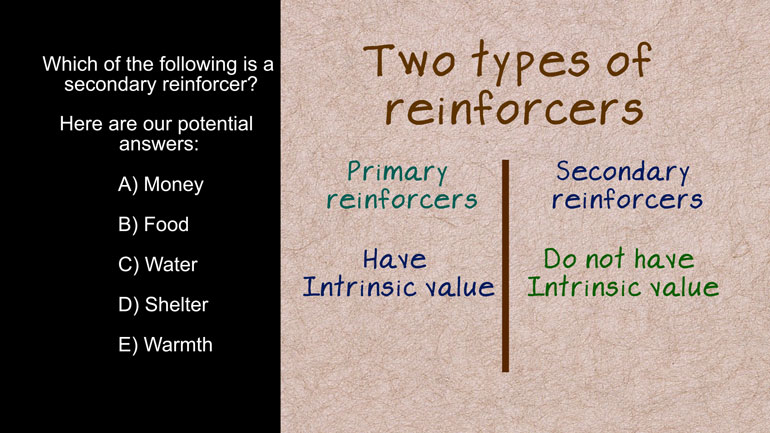
AP Psychology 3.3 Motivation and Emotion. When might using extrinsic rewards for motivation be harmful?
Transcript
- 00:03
Here's your shmoop du jour brought to you by Freudian slips
- 00:06
ideal for a young woman on the go particularly those interested in
- 00:10
attracting partners with oedipal complexes latency stages or imbalances
- 00:14
of the ideo or super-ego yeah it's a Freudian slip okay here's question when [Question appears]
- 00:20
might using extrinsic rewards for motivation be harmful?
Full Transcript
- 00:31
let's get into it what is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic
- 00:34
motivation well let's start with an example that deals with you the viewer
- 00:38
are you watching this video because you're trying to achieve a well-balanced [Boy reading books]
- 00:41
knowledge base or are you doing it to study psychology for a class or test
- 00:46
well if you're the first one you're probably not using your time correctly
- 00:49
and you're watching the video for intrinsic or internal motivations if [Boy appears with x-ray image over chest]
- 00:52
you're the second category and let's face it you probably are you're doing it
- 00:56
for extrinsic or external motivations yeah I guess at a and move on
- 01:00
extrinsic motivations or anything driven by external rewards to self refers to
- 01:05
financial incentives ie money but could also mean achievement ie grades a claim [Cash falling]
- 01:11
ie fame or adoration and praise ie well that one doesn't really need a synonym [People applauding]
- 01:17
so when would these wonderful things be harmful let's look at our options well
- 01:21
start with the two extreme answers a and E not the net worth in both tests in
- 01:25
psychology we normally find that extreme answers are problematic and these two [Man performing parkour]
- 01:28
are no exception the first would have us believe that rewards never work that
- 01:33
seems pretty naive especially since many of us have been working for extrinsic [Man riding a lawnmower]
- 01:37
motivation since our parents started tricking us into doing chores for small
- 01:41
allowances then we have answered e which says the opposite that offering rewards
- 01:44
always work never with any consequences and that seems pretty cynical even the
- 01:49
most trumpian people among us will probably admit that there are times when [Donald Trump outside Trump Tower]
- 01:52
offering extrinsic rewards can have negative consequences well that leaves
- 01:56
our middle options B C and D and let's look at B and C together because well
- 02:00
they're very similar beast has a person motivated by respect from his peers
- 02:03
doesn't need extrinsic motivation C says a person motivated by money doesn't need
- 02:09
extrinsic now as you may remember both money and [Donald Trump on a beach with money raining]
- 02:11
respect from peers are themselves extrinsic motivations albeit to viewed
- 02:15
very differently from society so each of these answers are basically saying that
- 02:19
those motivated by extrinsic motivations don't need extrinsic motivations that's [Woman making dog and monkey skip]
- 02:24
pretty confusing and it doesn't really make any sense even if we ignore the
- 02:27
problems in logic neither answer says why these motivations are harmful so
- 02:32
that brings us to D which says that if you're driven by personal motivation
- 02:35
external rewards might change your motives the first let's note that this
- 02:39
is the only one of the five answers which gives a clear reason for why [Answers appear on sheet]
- 02:42
extrinsic rewards are harmful second and more importantly let's note that this
- 02:46
one is true the ability of extrinsic rewards to interfere with personal [Man playing bass]
- 02:50
motivation is called the over justification effect simply put it means
- 02:55
that if someone enjoys something for purely personal reasons then is offered [People at a musical production]
- 02:59
a reward like money for that task their motivation will start to become reward
- 03:04
based rather than personal I should know I used to educate for the sheer thrill [Man teaching]
- 03:07
of it before shmoop came in with their promises of fame and fortune don't make
- 03:11
the same mistake I did don't let the riches and allure of academia keep you
- 03:15
from the self-satisfaction of learning
Related Videos
AP Psychology 1.1 Social Psychology. Which of the following best describes social psychology?
AP Psychology 1.1 States of Consciousness. Who conducted research on REM sleep deprivations?
AP Psychology 1.2 Cognition. Which of the following strategies would work best for generating new ideas?
AP Psychology 1.2 Sensation and Perception. The cells in the back of the eye that only see in black and white are called what?
AP Psychology 1.2 Social Psychology. What is the best choice for producing better productivity?